© 2019 Suzhou Tianzhijiao Precision Machinery Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved. Site Map Designed by iwonder.cn
The engine is the heart of the car, and its operating condition directly affects the performance and efficiency of the car. As one of the key components of the engine, the engine valve's working principle and structural characteristics are crucial to the normal operation of the engine.
The engine valve is mainly responsible for regulating the intake and exhaust flow. During the engine's working cycle, the valve accurately controls the opening and closing moments of the valve according to the movement of the piston and the rotation of the crankshaft. When the piston moves downward, the intake valve opens, allowing the air and fuel mixture to enter the cylinder; when the piston moves upward, the exhaust valve opens, allowing the burned exhaust gases to be discharged from the cylinder. Through such a cycle, the engine can continuously perform the four processes of intake, compression, combustion and exhaust to provide power.
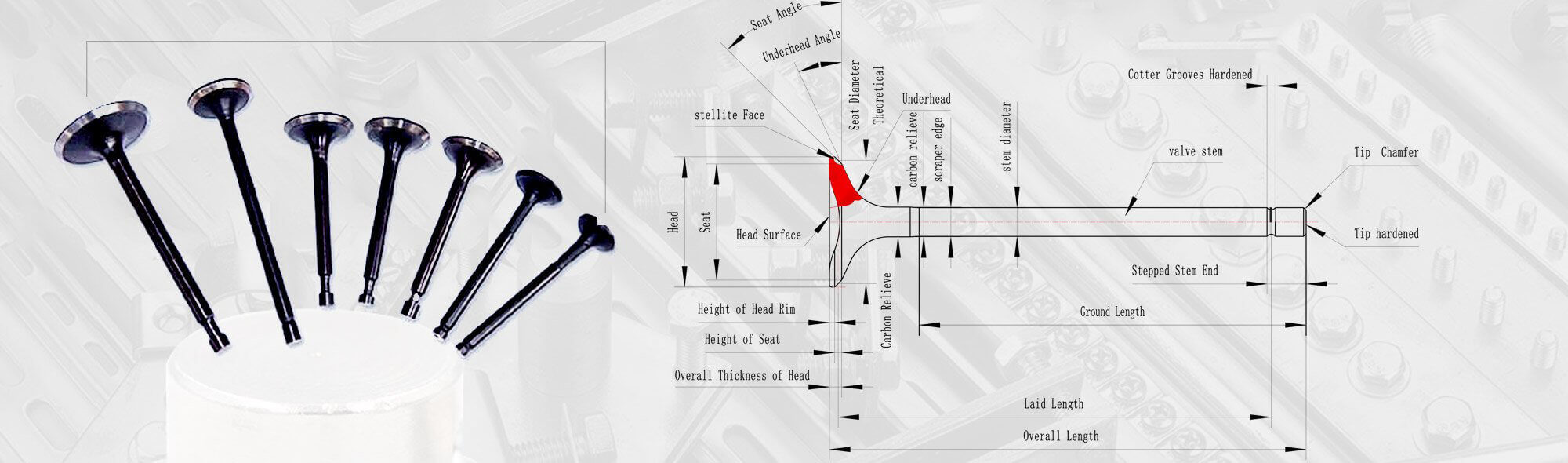
The structural design of the engine valve is also the key to realizing its working principle. Engine valves usually consist of valve chambers, valves, cylinder blocks and other components. The valve chamber is the space where the valve opens and closes. Its internal design must ensure the sealing and flexibility of the valve. The valve is a key component that controls the intake and exhaust flow. The selection of its shape and material is crucial to the durability and performance of the valve. The cylinder block plays the role of supporting and fixing the valve to ensure that the valve remains stable during high-speed operation.
As the core component of the automobile engine, the engine valve's normal operation is crucial to the smooth operation and performance of the engine. In actual use, engine valves may malfunction due to various reasons, such as valve sticking, poor sealing, etc. Therefore, maintenance personnel need to master certain professional knowledge and skills for valve fault diagnosis and repair.
There are many common types of engine valve failures. Among them, valve sticking is a common fault. When the engine valve valve fails to open or close normally, it may be due to carbon deposits, foreign matter obstruction, or poor lubrication. In addition, poor sealing is also one of the common faults of engine valves. When the seal between the valve and the valve seat is not tight, it will cause gas leakage and affect the engine's efficiency and performance.
Maintenance personnel need to initially judge whether there is a problem with the engine valve by observing the operating status of the engine, such as whether there are abnormal noises, jitters, or insufficient power. Then use professional diagnostic tools, such as oscilloscopes, cylinder pressure gauges, etc., to further detect the engine valves. By measuring and analyzing parameters such as valve opening and closing time, valve clearance, and valve sealing, the type and degree of engine valve failure can be more accurately determined. Once the type and extent of the engine valve failure is determined, the maintenance personnel need to take corresponding maintenance measures. The problem of valve sticking can be solved by cleaning carbon deposits, changing lubricating oil, or adjusting valve clearance. For problems with poor sealing, you need to check and replace worn parts, such as valves, valve seats or sealing gaskets. During the maintenance process, maintenance personnel need to pay attention to operating regulations and safety to avoid further damage to the engine.
Early Development: The earliest internal combustion engines used simple valve mechanisms such as slide valves or butterfly valves. These valves open and close inefficiently, limiting engine performance.
Mechanical valves: As technology develops, mechanical valves gradually replace earlier designs. Mechanical valves improve the control accuracy and reliability of the valve, but there are still certain limitations.
Turbo valve: A turbine valve is a design that uses a rotating valve core to increase the speed at which the valve opens and closes, thereby improving engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Application of new materials and new processes:
High-temperature alloys: In order to adapt to high-temperature and high-pressure environments, engine valves begin to use high-temperature alloy materials, such as molybdenum alloys, nickel-based alloys, etc., to improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the valves.
Coating technology: Through surface coating, the wear resistance and sealing performance of the valve can be improved, while friction loss can be reduced, and the efficiency and reliability of the engine can be improved.
Precision manufacturing process: Advanced manufacturing processes, such as CNC machining, laser cutting, etc., can improve the processing accuracy and surface quality of the valve, thereby improving the performance and reliability of the engine.
Variable valve timing technology: By adjusting the opening and closing times of the valves, the engine's intake and exhaust processes can be optimized, improving combustion efficiency and power output.
Valve lift control: Adjusting the valve lift can control the cylinder volume, thereby optimizing the engine's working process and improving fuel efficiency and power performance.
The role of engine valves in energy saving and emission reduction
Performance improvement: Innovation in engine valve technology can improve the combustion efficiency, power output and response speed of the engine, thereby improving overall performance and giving the vehicle better acceleration performance and driving stability.
Improved environmental performance: Advanced engine valve technology can reduce the production of emissions, reduce carbon emissions and nitrogen oxide emissions from cars, thereby reducing environmental pollution and meeting the environmental protection requirements of modern society.
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.